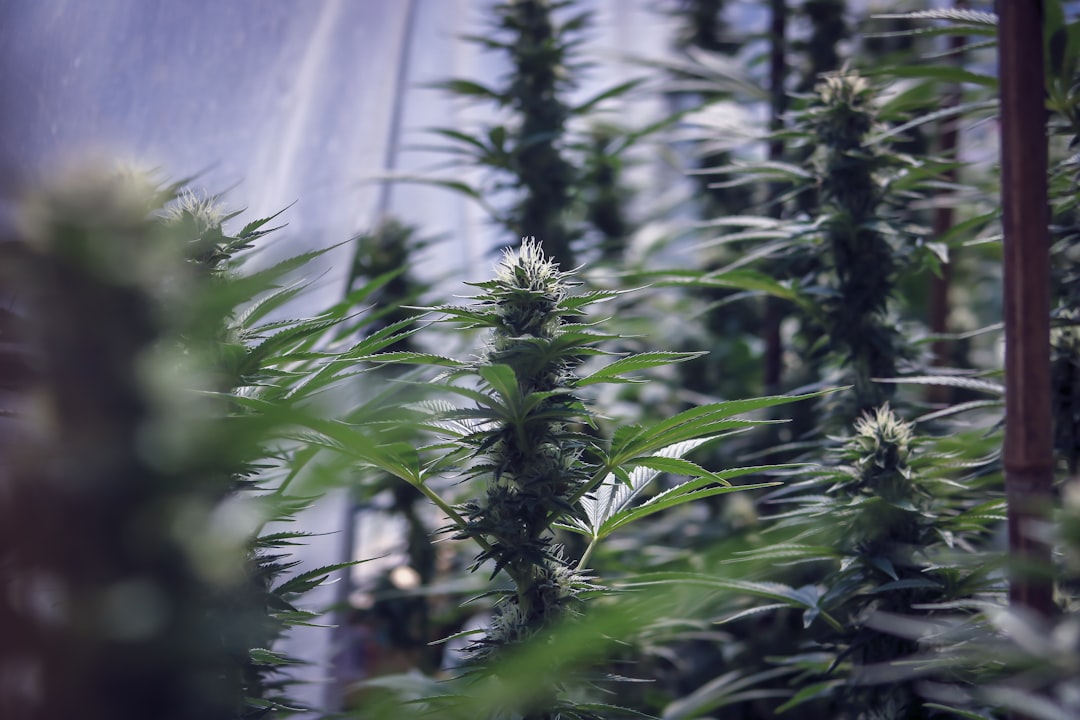
Sativa plants are one of the primary classifications of cannabis, distinguished by their unique characteristics that set them apart from their Indica and hybrid counterparts. Typically, Sativa strains are known for their tall, slender stature and elongated leaves, which contribute to their overall appearance. These plants thrive in warmer climates, often found in regions closer to the equator, where they can soak up ample sunlight.
The growth cycle of Sativa plants is generally longer than that of Indica varieties, which can be attributed to their genetic makeup and environmental adaptations. The chemical composition of Sativa strains also plays a significant role in their characteristics. They are often higher in THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) compared to CBD (cannabidiol), leading to a more cerebral and uplifting experience for users.
This is why many enthusiasts prefer Sativa strains for daytime use, as they tend to promote creativity, energy, and sociability. Understanding these fundamental traits is essential for both growers and consumers who wish to explore the diverse world of cannabis.
Key Takeaways
- Sativa plants are known for their tall and slender structure, with narrow leaves and long internodal spacing.
- Sativa plants originate from equatorial regions, such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Central America, and thrive in warm and humid climates.
- Sativa strains are characterized by their uplifting and energizing effects, making them popular for daytime use and creative activities.
- Sativa plants have a longer flowering time compared to indica and hybrid varieties, typically ranging from 10 to 16 weeks.
- Sativa plants are resilient against pests and diseases, making them suitable for outdoor cultivation in favorable climates.
Examining the Leaf Structure of a Sativa Plant
The leaf structure of Sativa plants is one of the most visually striking features that differentiate them from other cannabis varieties. Sativa leaves are typically long and narrow, with a serrated edge that gives them a distinct appearance. This leaf morphology allows for efficient photosynthesis, enabling the plant to maximize its energy intake during the long growing season typical of its native environments.
The light green color of Sativa leaves is also indicative of their high chlorophyll content, which is essential for robust growth. In contrast to Indica plants, which have broader leaves, Sativa leaves are designed to capture sunlight more effectively in open fields. This adaptation is crucial for survival in regions where competition for light is fierce.
The unique leaf structure not only contributes to the plant’s aesthetic appeal but also plays a vital role in its overall health and productivity. Observing these characteristics can provide valuable insights into the plant’s growth habits and environmental needs.
Noticing the Height and Growth Pattern of Sativa Plants
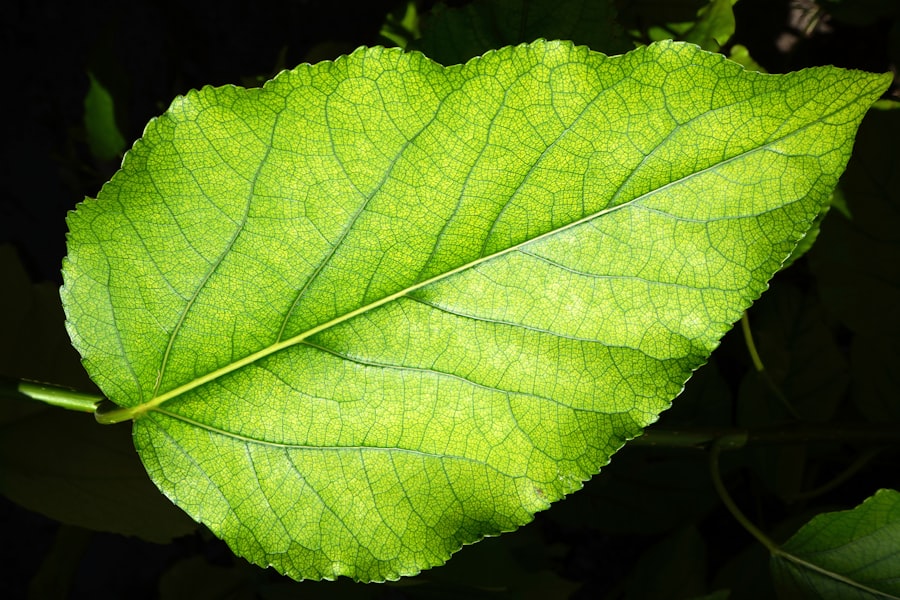

Sativa plants are renowned for their impressive height, often reaching upwards of six feet or more when fully matured. This vertical growth pattern is a result of their genetic predisposition to thrive in open environments where they can stretch towards the sun.
This characteristic makes them particularly well-suited for outdoor cultivation in regions with ample space. The growth pattern of Sativa plants is also influenced by their flowering cycle, which can take longer than that of Indica strains. Typically, Sativas may require 10 to 16 weeks to flower fully, depending on the specific strain and environmental conditions.
This extended growth period allows for the development of larger buds and a more complex cannabinoid profile. Growers must be patient and attentive during this phase, as the rewards can be substantial in terms of yield and potency.
Observing the Aroma and Flavor Profiles of Sativa Strains
One of the most captivating aspects of Sativa strains is their diverse aroma and flavor profiles. These strains often exhibit bright, fruity, and floral notes that can range from citrusy lemon to sweet berry undertones. The aromatic compounds responsible for these scents are known as terpenes, which not only contribute to the plant’s fragrance but also play a role in its effects.
For instance, strains high in limonene may provide uplifting sensations, while those rich in myrcene can offer relaxing qualities. The flavor experience of Sativa strains can be equally varied, with many users noting a refreshing and invigorating taste on the palate. This sensory appeal makes Sativa strains popular among cannabis connoisseurs who appreciate the nuances of different cultivars.
The combination of aroma and flavor not only enhances the overall experience but also reflects the plant’s unique genetic heritage and growing conditions.
Recognizing the Effects and Benefits of Sativa Cannabis
The effects of Sativa cannabis are often described as uplifting and energizing, making these strains ideal for social gatherings or creative endeavors. Users frequently report feelings of euphoria, increased focus, and enhanced motivation after consuming Sativa strains. This stimulating effect is primarily attributed to the higher THC content found in many Sativa varieties, which interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce these sensations.
In addition to recreational benefits, Sativa strains are also recognized for their potential therapeutic effects. Many users turn to Sativa cannabis for relief from conditions such as depression, anxiety, and chronic fatigue. The energizing properties can help combat lethargy and promote a more positive outlook on life.
As research into cannabis continues to evolve, more studies are likely to explore the specific benefits associated with various Sativa strains.
Identifying the Geographic Origins of Sativa Strains

Sativa cannabis has its roots in equatorial regions where the climate is warm and conducive to long growing seasons. Countries such as Colombia, Mexico, Thailand, and parts of Africa are known for producing some of the most iconic Sativa strains in history. These regions provide the ideal conditions for Sativa plants to flourish, with abundant sunlight and rich soil contributing to their robust growth.
The geographic origins of Sativa strains have also influenced their genetic diversity. Over time, local growers have cultivated unique varieties that reflect their specific environmental conditions and cultural practices. For example, Thai Sativas are renowned for their potency and distinct flavor profiles, while Colombian Gold is celebrated for its balanced effects and rich history.
Understanding these origins not only enhances appreciation for these strains but also informs growers about potential cultivation techniques suited to their local environments.
Differentiating Sativa Plants from Indica and Hybrid Varieties
Differentiating between Sativa, Indica, and hybrid cannabis varieties is essential for consumers seeking specific effects or cultivation characteristics. While Sativas are known for their tall stature and uplifting effects, Indica plants tend to be shorter and bushier with broader leaves. Indicas are often associated with relaxing effects that can help alleviate stress or promote sleep.
Hybrid strains combine characteristics from both Sativa and Indica plants, resulting in a wide range of effects depending on their genetic makeup. For instance, a hybrid strain with a higher percentage of Sativa genetics may produce energizing effects similar to pure Sativas, while those leaning towards Indica may offer more sedative qualities. Understanding these distinctions allows consumers to make informed choices based on their preferences or therapeutic needs.
Evaluating the Flowering Time and Harvesting Window of Sativa Plants
The flowering time of Sativa plants is one of the key factors that growers must consider when cultivating these strains. Generally speaking, Sativas require a longer flowering period compared to Indicas—often ranging from 10 to 16 weeks before they are ready for harvest. This extended timeline can be attributed to their genetic traits and growth patterns, which allow them to develop larger buds and more complex cannabinoid profiles.
Growers must be patient during this phase, as rushing the harvest can lead to suboptimal yields or potency levels. Monitoring trichome development is crucial; when they turn from clear to milky white or amber, it indicates that the plant is nearing peak maturity. Understanding this timeline not only helps growers optimize their harvest but also ensures that consumers receive high-quality products with desired effects.
Considering the Environmental Preferences and Growing Conditions of Sativa Strains
Sativa strains thrive in specific environmental conditions that mimic their native habitats. These plants prefer warm temperatures with plenty of sunlight—ideally between 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C). They also benefit from well-draining soil rich in nutrients, which supports healthy root development and overall growth.
For indoor growers, providing adequate lighting through high-intensity discharge (HID) or LED lights can replicate natural sunlight conditions. Outdoor cultivation is often preferred for Sativas due to their height and space requirements; however, growers must be mindful of local climate conditions such as humidity levels and rainfall patterns. Excess moisture can lead to mold or mildew issues during flowering, so proper ventilation and airflow are essential considerations.
By understanding these environmental preferences, growers can create optimal conditions that promote healthy growth and maximize yields.
Recognizing the Sativa Plant’s Resistance to Pests and Diseases
Sativa plants exhibit certain traits that contribute to their resilience against pests and diseases. Their tall stature allows for better airflow around the plant, reducing humidity levels that can foster mold growth or attract pests like spider mites or aphids. Additionally, many Sativa strains have developed natural defenses over time due to their exposure to various environmental pressures in their native habitats.
However, it is important for growers to remain vigilant against potential threats even with these inherent advantages. Regular inspections for signs of pests or diseases can help catch issues early before they escalate into larger problems. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies—such as introducing beneficial insects or using organic pesticides—can further enhance a grower’s ability to maintain healthy plants throughout the cultivation process.
Understanding the Cultivation and Breeding History of Sativa Cannabis
The cultivation and breeding history of Sativa cannabis is rich and complex, reflecting centuries of human interaction with this versatile plant. Historically, indigenous cultures have utilized cannabis for various purposes ranging from medicinal applications to spiritual rituals. As cannabis spread across different regions, local growers began selectively breeding plants based on desired traits such as potency, flavor profiles, or growth characteristics.
In modern times, advancements in breeding techniques have led to an explosion of new Sativa strains that cater to diverse consumer preferences. Breeders now employ methods such as crossbreeding and genetic testing to create hybrids that combine desirable traits from both Sativa and Indica varieties. This ongoing evolution continues to shape the landscape of cannabis cultivation while providing enthusiasts with an ever-expanding array of options.
In conclusion, understanding the characteristics of Sativa plants offers valuable insights into their unique attributes and benefits within the cannabis community. From their distinctive leaf structure and impressive height to their uplifting effects and diverse flavor profiles, Sativas hold a special place among cannabis enthusiasts worldwide. By recognizing their geographic origins, environmental preferences, and cultivation history, both growers and consumers can appreciate these remarkable plants on a deeper level.
If you are interested in learning more about sativa plants, you may want to check out the article on Sativa Learning. This website offers valuable information on identifying and understanding different strains of cannabis, including sativa plants. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced grower, Sativa Learning can provide you with the knowledge and resources you need to successfully cultivate and enjoy sativa plants.